Benjamin Franklin once said, “Investment in knowledge pays the best interest”. Although Benjamin Franklin lived in the 18th century, his words are still relevant today.
However, the total cost of investing in knowledge would look quite different in the 21st century.
How much should a parent expect to pay for one child’s education journey from preschool to university?
We take a closer look at the average total cost of education in Singapore, for both public (government schools, unless otherwise stated) and private schools (including international schools).
(All figures are quoted in Singapore dollars.)
Average Total Cost of Education in Singapore (2024)
The average total cost of education in Singapore is $71,409.
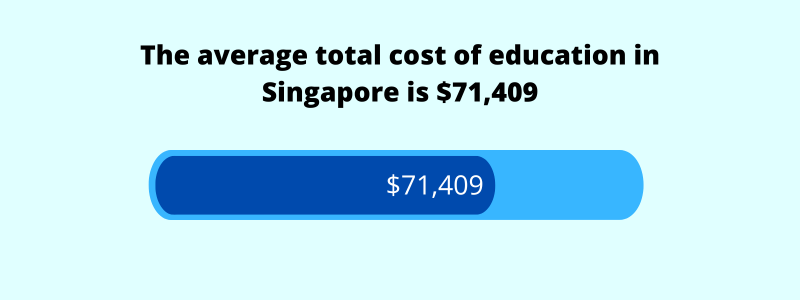
The above estimate is based on a few assumptions:
- The child is a Singapore Citizen
- Infant care (full-day) provided by an ECDA-licensed centre (AOP) for 16 months: $10,140.80 (after subsidies with the median household income)
- Child care (full-day) provided by an ECDA-licensed centre (AOP) for 66 months: $20,090.40 (after subsidies with the median household income)
- Primary school for 6 years: $936
- Secondary school for 4 years: $1,200
- Junior college for 2 years: $792
- University for 4 years: $38,250
The estimate also assumes that the child only attends government schools. The estimate doesn’t include the cost of living as a student and other miscellaneous items, such as textbooks, stationeries, uniforms, and excursions. It also reflects the current costs and doesn’t factor in inflation, so expect those figures to increase in the future.
For PRs and international students, expect to pay many multiples of that estimate.
Read on to learn more about the school fees for the various levels of education.
SIDE NOTE When was the last time you conducted thorough financial planning or reviewed your finances? In this day and age in Singapore, doing so will absolutely improve the quality of life for you and your loved ones. Here are 5 reasons why financial planning is so important.
The Education System in Singapore
In Singapore, education is treated as a basic right that all children are entitled to, regardless of their social class.
The government goes to great lengths to ensure that all children are able to receive an education in order to thrive in the world. In fact, all parents are required by law to enrol their children into primary schools under the Compulsory Education Act.
Typically, this is the education journey of school-going children in Singapore.
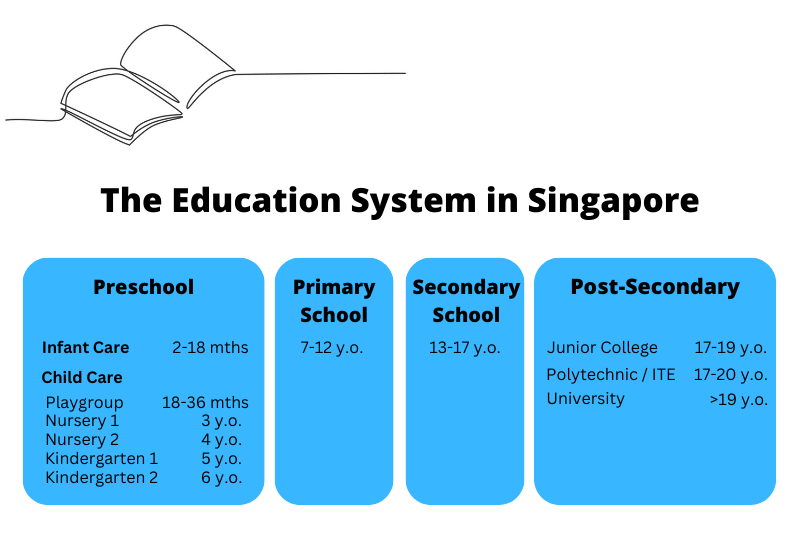
Most of the children in Singapore go through this route. However, there might be certain variations.
For example, some children might not go to infant care or playgroup during their preschool years. At the secondary school level, students can also opt to enrol in Integrated Programme (IP) schools where they do not have to sit for a national exam during their 4th year, and only take the A-Level exams in their 6th year. Others might enrol in International Schools that offer the International Bachelorette (IB) that also follows a 6-year programme. Finally, the post-secondary education route has the most variations depending on the students’ readiness levels.
Depending on your child and your family beliefs about education, you may be planning to set aside money for at least until your child’s undergraduate school fees and/or only until they achieve a diploma at the Polytechnic level.
How Has the Cost of Education Changed Over the Years
The cost of living in Singapore has been a hot topic.
In a healthy economy, there should be inflation – prices of goods and services increase over a period of time. According to MAS, Singapore’s inflation should be kept moderate, and not be at extremes.
The cost of education, in general, has been steadily rising over the years.
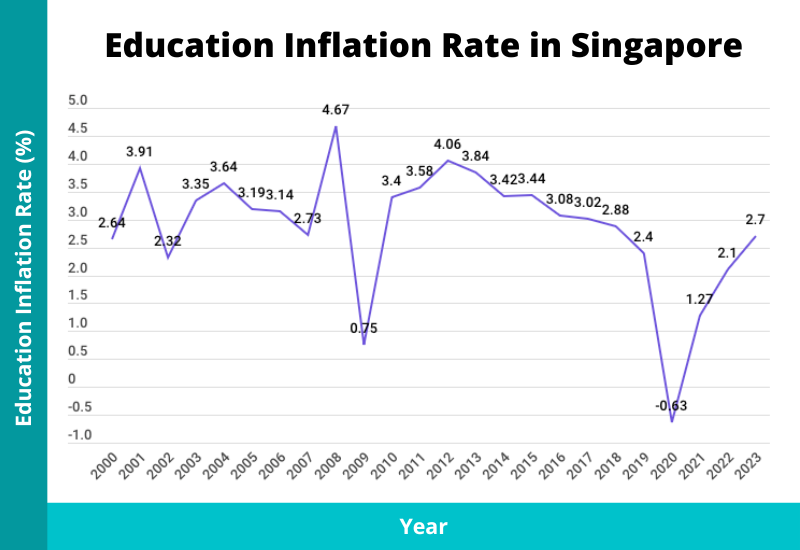
From 2003 to 2023, the cost of education increased by 74.7%.
Although we are seeing abnormally high inflation in recent years, over the past 20 years, the average education inflation rate was 2.83% per year.
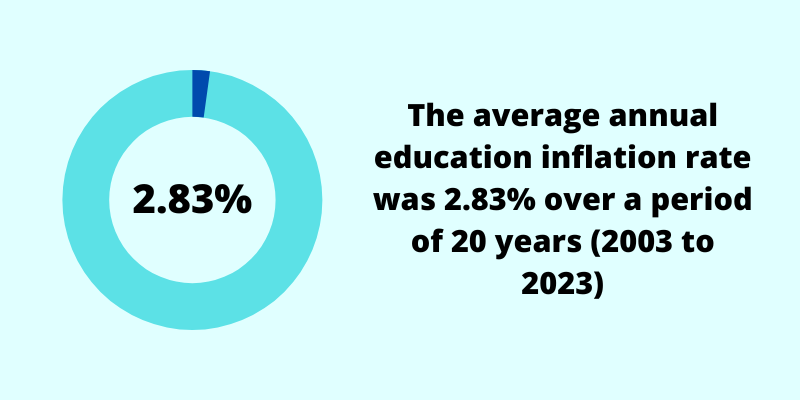
Below, we point out the current fees for various education levels, but you should expect these figures to increase with time.
School Fees For Various Education Levels
Preschool
With the increasing number of dual-income family models in Singapore, more and more Singaporean children are enrolled in preschool so that their parents can go to work during the day.
If this is a decision that you and your spouse make, be prepared to set aside a hefty sum of money for your child.
These are the school fees for the different grade levels – infant care, child care, and kindergarten – at the various ECDA-subsidised or private preschools.
| Grade/Level | ECDA schools (AOP) | Private schools & others | Average cost per month (after subsidies) |
| Infant Care (Full Day) | $1,333.80 | $1,201 – $2,600.10 | Between $40 – $2,400 |
| Child Care (Full Day) | $734.40 | $800 – $2,321.90 | Between $3 – $2,000 |
| Kindergarten | $162 | $800 – $2,321.90 | Between $3 – $2,000 |
Any Singapore Citizen child enrolled in an ECDA-licensed infant or child care centre is eligible for subsidies. The amount of subsidies given depends on the family’s household income and whether the applicant (usually the mother) is working or not.
For infant care, working applicants can receive a basic subsidy of $600 and an additional subsidy of up to $710. Non-working applicants can receive a basic subsidy of $150 but no additional subsidies.
For child care, working applicants can receive a basic subsidy of $300 and an additional subsidy of up to $467. Non-working applicants can receive a basic subsidy of $150 but no additional subsidies.
(Note: You can use this nifty subsidy calculator created by ECDA.)
How much would this all work out? Let’s assume your household income is the national average (median) of $10,099 per month, the mother is working, and the infant or child care centre is under the AOP.
If you have chosen to fully enrol your child in preschool since two months old, you can expect to pay a total of $10,140.80 (infant care for 16 months) and $20,090.40 (child care for 66 months) = $30,231.20 for their preschooling years (after subsidies).
In comparison, if you have the means to provide caregiving to your child up to 18 months old, you can expect to pay a total of $20,090.40 (child care for 66 months) for their preschooling years (after subsidies).
The cost for preschool education is hefty. Choosing schools wisely will help to ensure that you have enough money to pay for education in the later years of your child’s life.
Primary School
Thanks to the Compulsory Education Act, this is where many parents can heave a sigh of relief about the payment of school fees.
The cost is almost negligible as all Singaporean Citizens are entitled to free primary school education in Singapore. Parents will only need to pay a monthly miscellaneous fee (that goes to the school’s operating budget) of between $6.50 – $13, depending on the school’s needs. You may check the school fees you are required to pay for each child on MOE’s website.
For PRs, the monthly school fees are set at $230 – $268. For international students, the cost for ASEAN-member students is $490 – $528, and $825 – $888 for non-ASEAN students.
The table below gives you the final sum of primary school fees for 6 years, assuming that these fees do not rise in the next few years.
| Residency Status | Monthly Fee | Total Cost for 6 years (72 months) |
| Singaporean Citizen | $6.50 – $13 | $468 – $936 |
| Singapore PR | $230 – $268 | $16,560 – $19,296 |
| International (ASEAN) | $490 – $528 | $35,280 – $38,016 |
| International (non-ASEAN) | $825 – $888 | $59,400 – $63,936 |
For a Singapore Citizen, the total cost for 6 years of primary school education is $936 in a government or government-aided school.
(Note: While there’s a range in the monthly fee, most schools have fees in the upper limit.)
Secondary School
Secondary schools in Singapore are split into 5 types: government schools, government-aided schools, independent schools, specialised independent schools (e.g. SOTA), and special education schools.
The amount of school fees payable depends on the type of secondary school your child is enrolled in. The table below presents the maximum fee for 4 years of secondary school education.
The fees for specialised independent schools and special education schools are not provided as these are dependent on the individual school themselves.
| Status | Government or Government-aided school [GS or GAS] (monthly fee) | Independent School [IS] (monthly fee) | Total cost for 4 years (48 months) of GS or GAS | Total cost for 4 years (48 months) of IS |
| Singaporean Citizen | $5 – $25 | $300 – $600 | $1,200 | $28,800 |
| Singapore PR | $440 – $520 | $600 – $1000 | $24,960 | $48,000 |
| International (ASEAN) | $840 – $920 | $1,000 – $2,500 | $44,160 | $120,000 |
| International (non-ASEAN) | $1,600 – $1,770 | $1,000 – $2,500 | $84,960 | $120,000 |
For a Singapore Citizen, the total cost for 4 years of secondary school education is $1,200 in a government or government-aided school.
Looking at the price difference, it might make sense for a Singaporean parent to choose government or government-aided schools for their child.
The total difference in payment between these two types of schools and an international school is a whopping $27,600. This is no small figure.
Given the improving landscape of education in Singapore and the professionalisation of teachers across all schools, it would not make a huge difference to your child should you decide to enrol them in a government school.
Furthermore, as our Education Ministers like to say, “Every school is a good school”.
Post-Secondary Education
There are 3 different routes a student can take for post-secondary education: Junior College, Polytechnic and Institute of Technical Education (ITE). These are the school fees you can expect to pay for each different route.
DID YOU KNOW? According to a survey conducted by MoneySense, about 3 out of 10 Singapore residents aged 30 to 59 had not started planning for their future financial needs. This isn't surprising because personal finance can seem complicated and daunting. But really, there are only a few things that you should focus on. Learn how to significantly improve your personal finances with the 7-step "wedding cake" strategy today.
Junior College
At the junior college (JC) level, education is still heavily subsidised. The monthly school fees for Singaporeans are set at $6, while the monthly miscellaneous fees are $13.50 – $27. Most students spend 2 years at JC (except for Millenial Institute students). The table below illustrates the total cost one can expect to pay if enrolling your child in a JC in Singapore.
| Residency Status | Monthly Fee | Total Cost (24 months) |
| Singaporean Citizen | $6 – $33 | $792 |
| Singapore PR | $520 – $607 | $14,568 |
| International (ASEAN) | $1,070 – $1,127 | $27,048 |
| International (non-ASEAN) | $1,950 – $2,127 | $51,048 |
For a Singapore Citizen, the total cost for 2 years of junior college education is $792.
Polytechnic
Students at the polytechnic will graduate with a diploma. The polytechnics adopt a “cohort-based fee structure”, and the government continues to absorb the GST chargeable on tuition fees payable by Singapore Citizen students. Students at the polytechnic typically spend 3 years on their full-time diploma course. The table below illustrates the total cost one can expect to pay if your child decides on taking the Polytechnic route.
| Residency Status | Annual Fee | Total Cost (3 years) |
| Singaporean Citizen | $3,000 | $9,000 |
| Singapore PR | $6,200 | $18,600 |
| International (ASEAN) | $11,900 | $35,700 |
| International (non-ASEAN) | $11,900 | $35,700 |
For a Singapore Citizen, the total cost for 3 years of polytechnic education is $9,000.
Institute of Technical Education (ITE)
The third route that Singapore offers is a course at ITE. Students who are more technically gifted often choose to go to ITE to be armed with technical skills that would prepare them well for their vocation. At ITE, students will pay the fees according to the courses they choose.
These range from Nitec to Higher Nitec and a Technical Diploma in the specialised field. The figures below exemplify the various fees at ITE College Central.
Singapore Citizen
| Nitec | $430 |
| Higher Nitec | $590 |
| Technical Engineering Diploma | $3,000 |
| Technical Diploma in Culinary Arts | $3,310 |
Singapore PR
| Nitec | $6,150 |
| Higher Nitec | $7,760 |
International Students (ASEAN and non-ASEAN)
| Nitec | $17,400 |
| Higher Nitec | $20,550 |
Nitec and Higher Nitec courses are typically 1 – 2 years long. This means that a Singaporean parent can expect to pay between $820 – $1180 for the 2 years that the child is undergoing the Nitec certification course. This is relatively cheaper than polytechnic courses and provides the child with the key skills required for the vocation of their choice.
| Residency Status | Annual Fee | Total Cost (2 years) |
| Singaporean Citizen | $430 – $590 | $860 – $1,180 |
| Singapore PR | $6,150 – $7,760 | $12,300 – $15,520 |
| International (ASEAN) | $17,400 – $20,550 | $34,800 – $41,100 |
Universities
Every parent hopes to send their child to university and allow them to graduate with a degree that would open the doors to many opportunities.
In Singapore, there are 6 local universities (NUS, NTU, SUTD, SUSS, SIT, SMU) and private universities (e.g., SIM Global) that Singaporean students can pursue further studies.
Local universities are relatively cheaper when it comes to tuition fees, and the degrees are recognised across the world.
Each university’s tuition fees differ and are largely dependent on these two factors:
- Type of degree (you can expect to pay more for medicine/dentistry/law)
- Year of enrolment (fees typically increase every year)
A study of the different tuition fees in Singapore revealed the following data – parents have to set aside an average of $38,250 for a four-year general undergraduate degree.

For Singaporean citizens enrolled in local universities for AY2023/2024, the table below depicts the total estimated school fees.
| School | Annual Course Fees | Total Estimated Course Fees | Average Course Fees |
| NUS | $8,250 to $9,650 | $33,000 to $38,600 | $35,800 |
| NTU | $8,250 to $9,450 | $33,000 to $37,800 | $35,400 |
| SMU | $11,500 | $46,000 | $46,000 |
| SUTD | $13,500 | $54,000 | $54,000 |
| SIT | – | $22,500 to $37,200 | $29,850 |
| SUSS | – | $30,000 to $33,640 | $31,820 |
| Overall | $8,250 to $13,500 | $22,500 to $54,000 | $38,250 |
For a more detailed breakdown of the cost of university education in Singapore, please click here.
International Schools
If you’re an expat in Singapore, you are likely to have heard of familiar international schools that follow the curriculum in your country of origin.
Some of the more well-known international schools are the Australian International School, Lycee Francais de Singapour (The French School of Singapore) and the German European School Singapore.
These schools offer education from preschool levels all the way to the pre-university level.
However, be prepared to pay a high fee, with no subsidy from the Singapore government.
A quick look at the German European School 2023/2024 school fees reveals the following school fees for the different grade levels.
| Grade | Annual Fees (exclusive of entrance and miscellaneous fees) |
| Preschool (Pre-Kindergarten, K1 & K2, Pre-Primary) | $35,550 |
| Primary School | $37,720 |
| Middle School | $41,645 |
| High School | $46,490 |
Final Thoughts
Receiving an education is one of the best gifts we can give our children.
However, this also means that we need to plan our finances carefully to ensure that we can meet their needs and provide them with the best opportunities as they undertake their schooling years.
For a typical Singaporean child who starts their journey at the preschool level (from infant care), goes through primary and secondary school, and junior college, before undertaking a four-year degree at a local university, the entire journey could cost $71,409.20. This does not include the cost of living and other miscellaneous items, such as textbooks and stationeries.
Thus, it is essential to plan and set aside money for school fees, and additional cash for other materials like textbooks, uniforms, school excursions, etc.


